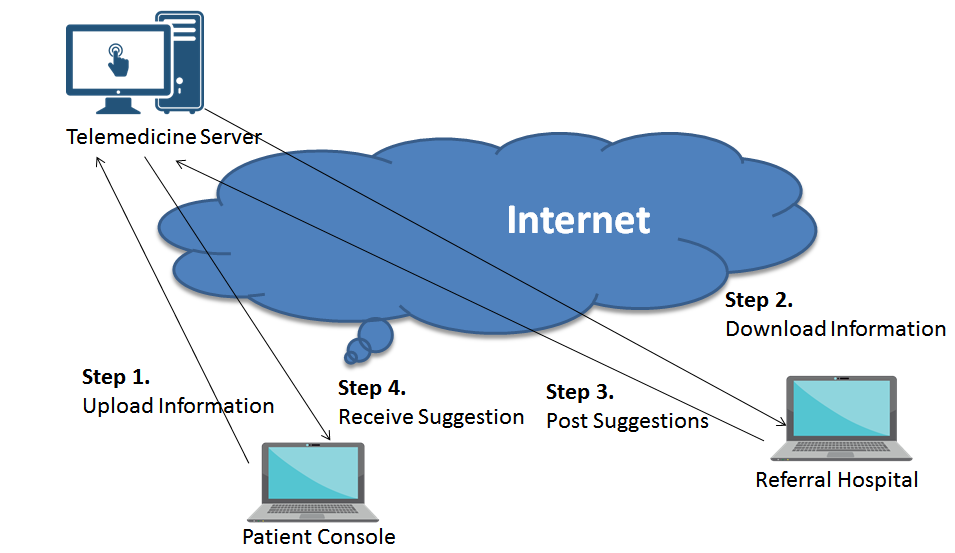
HOW IT WORKS

- Video conference system
- Cameras each end
- TV screens/computers each end
- Various medical peripherals
- Video connection
- T-1 line
- Satellite
- Phone line (POTS)
- Internet
EXCHANGE OF INFORMATION AT A DISTANCE
- Voice
- Image
- Video
- Graphics
- Elements of Medical Records
- Commands to a surgical robot
TECHNOLOGIES INVOLVED
Medical Instrumentation- Sensing Bio-medical Signals,
- Medical Imaging, Measurement of Physical
- Parameters e.g. Body Temperature, Pressure etc.
- Trans-receiver on different communication
- channels and network such as, on wired network, wireless medium etc.
- Information representation, storage, retrieval, processing, and presentation.
APPLICATIONS
- Information exchange between Hospitals and Physicians.
- Networking of group of hospitals, research centers.
- Linking rural health clinics to a central hospital.
- Videoconferencing between a patient and doctor, among members of healthcare teams.
- Training of healthcare professionals in widely distributed or remote clinical settings.
- Instant access to medical knowledgebase, technical papers etc.
REQUIREMENT SPECIFICATION
 |
|
|
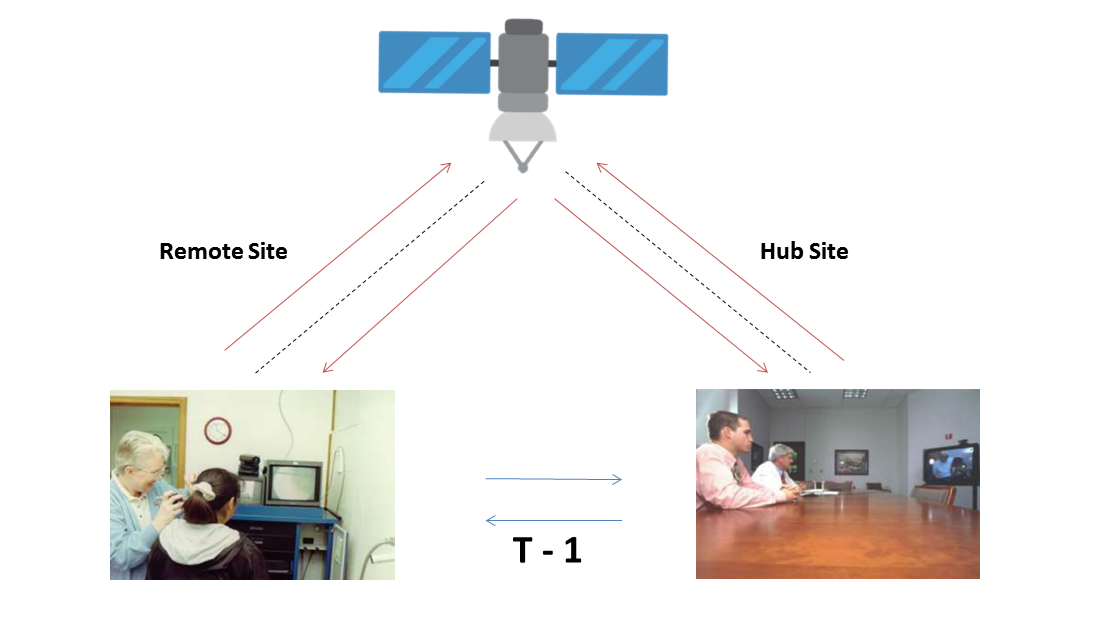
2 - WAY TELEMEDICINE
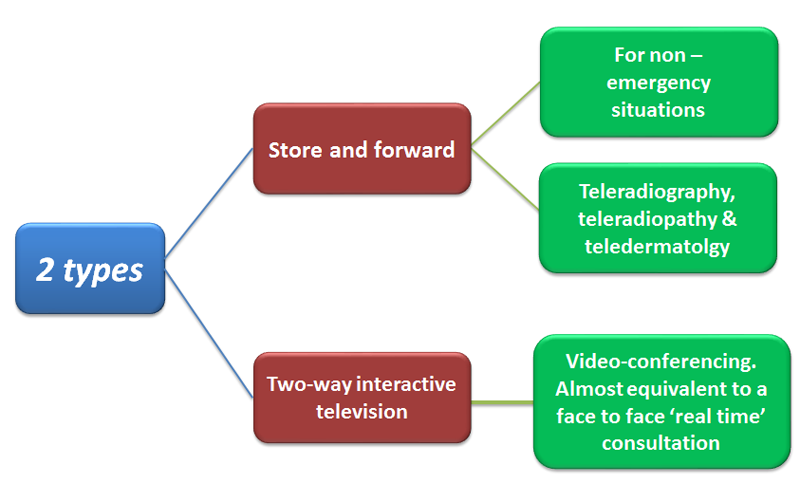
SEQUENCE OF OPERATION

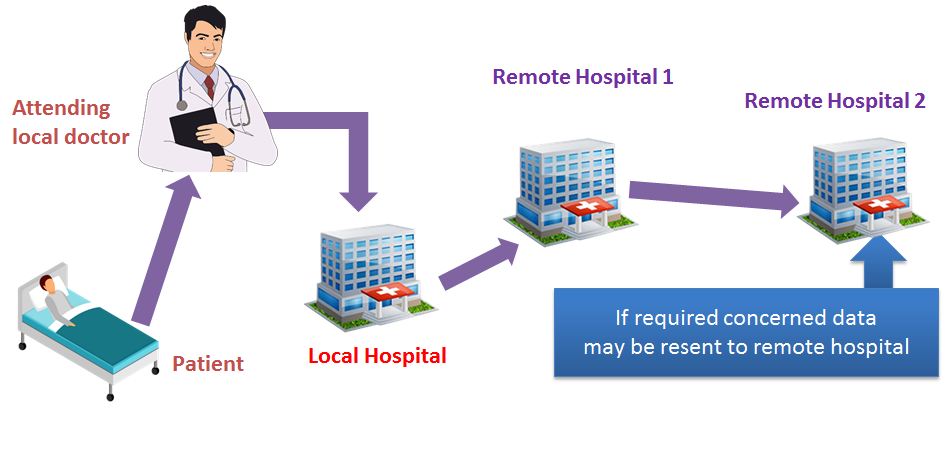
MULTI-REFERENCE IN TELE-CONSULTATION
A center acting as local asks for tele-consultation with a remote center which can again be able to consult with another remote center.
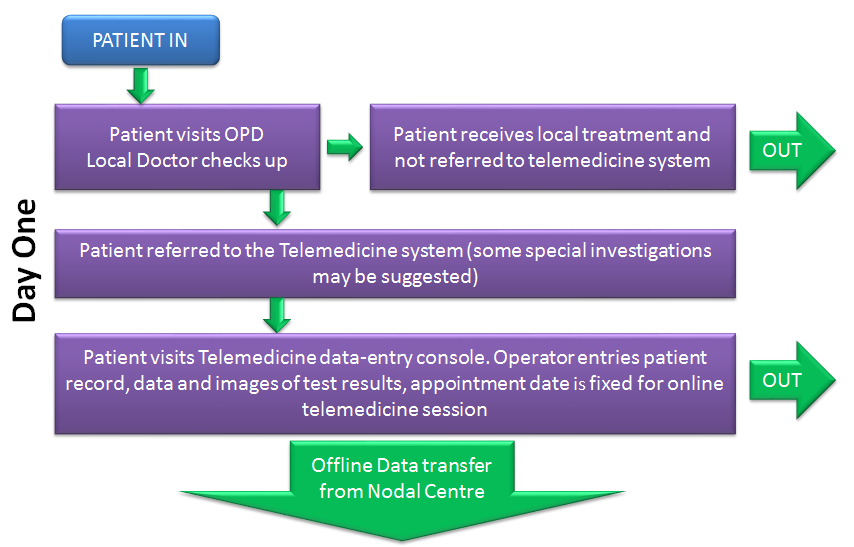
TELEMEDICINE OVER WEB